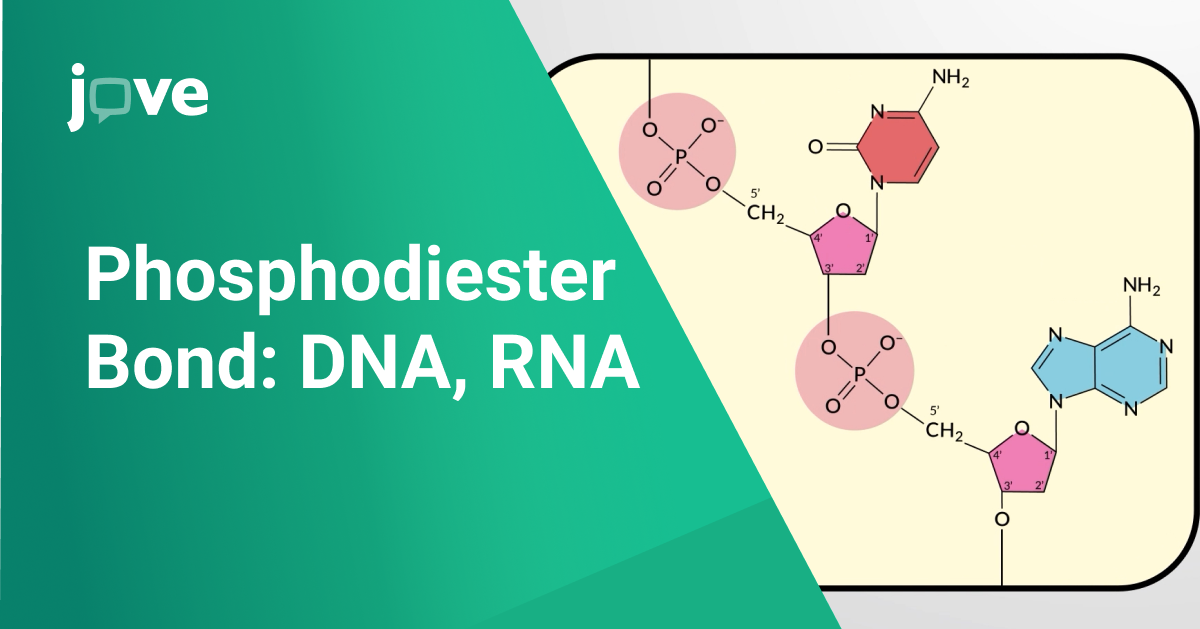
What are Phosphodiester bonds?
Phosphodiester bonds are a type of covalent bond essential for the structural integrity of both DNA and RNA molecules. These bonds connect nucleotides, forming the backbone of nucleic acid chains. By linking the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the sugar molecule of the next, they ensure the stability and functionality of the genetic material, allowing it to store and transmit genetic information effectively. In summary, phosphodiester bonds are like the sturdy threads that string together the beads (nucleotides) of the DNA necklace, ensuring it remains intact and functional.
How are phosphodiester bonds formed?
Phosphodiester bonds are formed through a condensation reaction, also known as dehydration synthesis. During DNA replication or RNA transcription, enzymes like DNA polymerase or RNA polymerase facilitate this process. The reaction involves the 3' hydroxyl group of the sugar of one nucleotide reacting with the 5' phosphate group of the incoming nucleotide, releasing a molecule of water in the process. This creates a continuous sugar-phosphate backbone along the nucleic acid strand.
Where is the phosphodiester bond in DNA?
In a single strand of DNA, phosphodiester bonds link all the nucleotides end to end. When DNA forms a double-stranded structure, two such chains run in opposite directions (antiparallel) and are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases (A-T and G-C). While the hydrogen bonds stabilize the pairing of the bases, the phosphodiester bonds are responsible for the continuity and stability of each DNA strand's backbone. This combination of bonds ensures that the DNA molecule is both stable and flexible, allowing it to carry out its vital biological function
Learning with Jove.com
To gain a deeper understanding of phosphodiester bonds and their role in DNA and RNA, watching educational videos on Jove.com can be extremely helpful. Jove offers a range of high-quality, peer-reviewed video articles that visually explain complex biological processes, including the formation and function of phosphodiester bonds. These videos can provide a more dynamic and engaging learning experience, helping to solidify your grasp of the concepts through visual aids and detailed explanations.
Conclusion about the Phosphodiester Bond Linkage: A Curiosity
The phosphodiester bond linkage is not only crucial for the structure and function of nucleic acids but also fascinating in its biochemical precision and resilience. Each bond forms through a condensation reaction, where a water molecule is released, linking the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the hydroxyl group of another. What’s particularly intriguing is how these bonds create a stable yet flexible backbone that can withstand various environmental conditions while preserving the integrity of the genetic information. Additionally, the enzymes that catalyze the formation and breaking of these bonds, such as DNA polymerases and nucleases, exhibit remarkable specificity and efficiency, highlighting the intricate complexity of molecular biology. Understanding these bonds opens up a world of curiosity about how life stores and transmits information at a molecular level.