The therapeutic index (TI) is a crucial concept in pharmacology, representing the safety margin of a drug. It is a measure of the drug's safety, defined as the ratio between the toxic dose and the therapeutic dose. Understanding the therapeutic index helps in determining the appropriate dosage of a drug to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. In this blog post, we will explore what the therapeutic index is, its significance, how it is calculated, and its implications in drug development and clinical practice.
What is the Therapeutic Index?
The therapeutic index is a numerical value that indicates the safety of a drug by comparing the dose that causes toxicity to the dose that provides therapeutic benefits. A higher therapeutic index indicates a larger margin of safety, meaning the drug can be administered with less risk of causing harmful side effects.
How to calculate the Therapeutic Index formula?
The therapeutic index is typically calculated using the following formula:
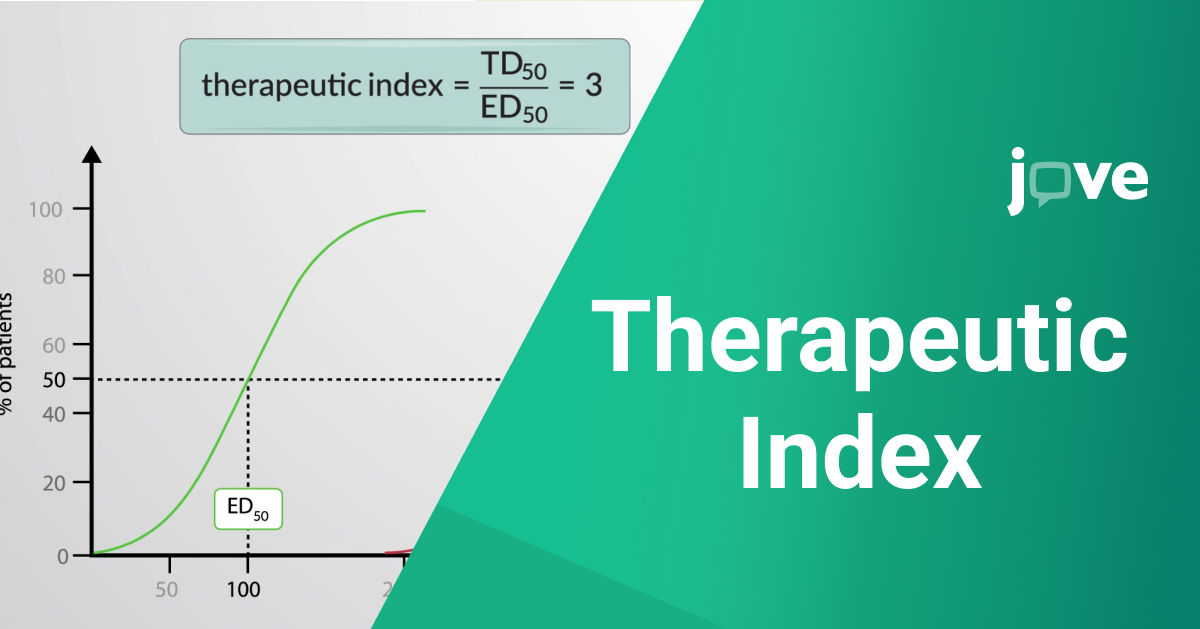
Therapeutic Index (TI)=TD50ED50\text{Therapeutic Index (TI)} = \frac{\text{TD}_{50}}{\text{ED}_{50}}Therapeutic Index (TI)=ED50TD50. Were:
- TD50 (Toxic Dose 50%): The dose of the drug that causes toxicity in 50% of the population.
- ED50 (Effective Dose 50%): The dose of the drug that produces a therapeutic effect in 50% of the population.
- In some cases, the lethal dose (LD50), which is the dose that causes death in 50% of the population, is used instead of TD50, especially in preclinical studies involving animal models.
Examples of Therapeutic Index in Practice
To better understand the practical applications of the therapeutic index, it's important to consider specific examples of drugs with high and low therapeutic indices.
-
High TI Drugs: Drugs with a high therapeutic index, such as penicillin, are considered safer because the effective dose is much lower than the toxic dose. These drugs can be administered with less concern for toxicity at therapeutic doses.
-
Low TI Drugs: Drugs with a low therapeutic index, such as warfarin and digoxin, have a narrow safety margin. These drugs require careful monitoring and precise dosing to avoid toxicity while achieving therapeutic benefits.
Conclusion
The therapeutic index is a fundamental concept in pharmacology that guides the safe and effective use of drugs. By providing a measure of the safety margin, the TI helps in optimizing dosage regimens, assessing risk, and ensuring patient safety. Understanding the therapeutic index is essential for clinicians, researchers, and anyone involved in drug development and therapy management. As we advance in the fields of personalized medicine and pharmacogenomics, the precise determination and application of the therapeutic index will continue to play a vital role in improving therapeutic outcomes and patient care.